If you work around compressed gas such as nitrogen, helium, and propane it is essential that you understand the key components of compressed gas safety.
To help you better understand compressed gas safety, this article will examine what compressed gas safety is, how you can handle compressed gas products safely, and what to do in an emergency situation involving compressed gas.
Click on each corresponding link to learn more:
- What Is Compressed Gas Safety?
- How Can you Handle Compressed Gas Products Safely?
- What to Do in an Emergency Situation
ACUTE Environmental is your go-to resource for all things safety training. Simply contact us today to set up your safety training!
An Overview of Compressed Gas Safety

Continue reading to learn more about compressed gas safety.
1. What Is Compressed Gas Safety?
Compressed gas safety refers to a set of practices and precautions designed to ensure the safe handling, storage, and use of gases that are stored in compressed form, typically in cylinders or containers. Compressed gases are commonly used in various industrial, scientific, medical, and commercial applications, but they can be hazardous if not handled properly.
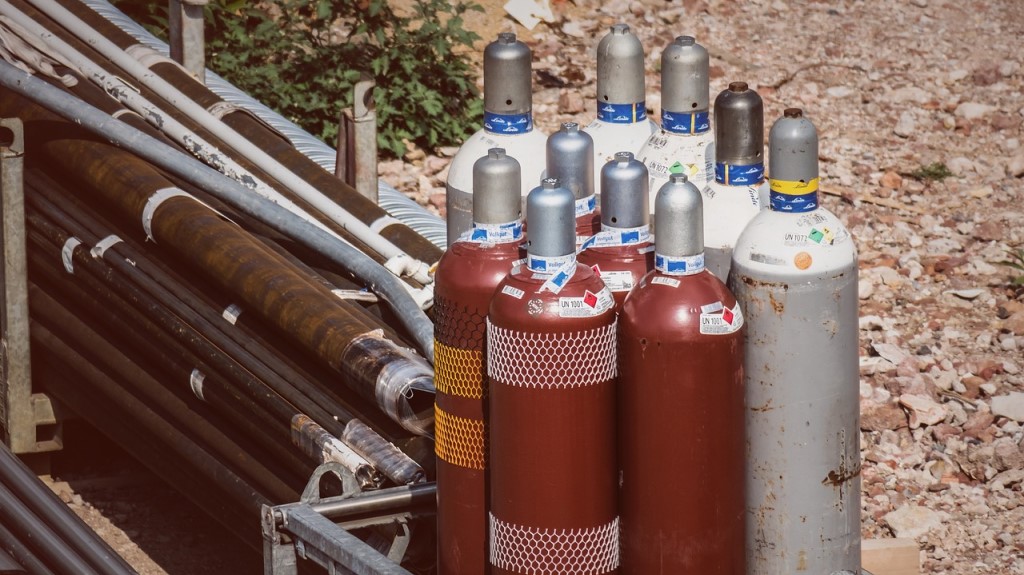
Hazardous products with the gas cylinder pictogram (displayed on the right) are “gases that are contained in a receptacle under pressure, or which are liquefied or liquefied and refrigerated”.

You may also be wondering what products contain the gas cylinder pictogram. If this is the case, here is a table provided by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety outlining the types of products that are assigned this pictogram:
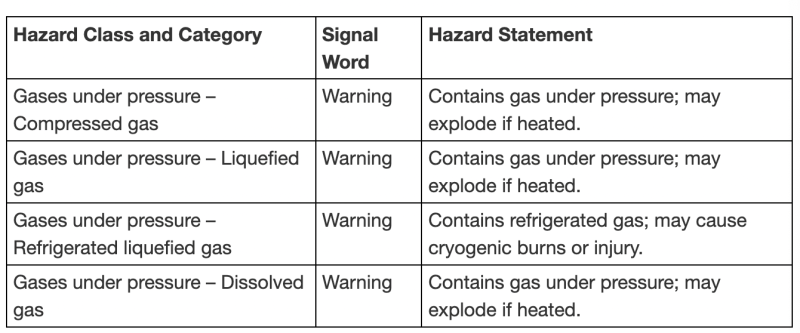
Consider this chart and learn more about compressed gas safety.
A) Examples of Compressed Gases in the Workplace



Here is a breakdown of these images:
- The first image is of Acetylene (C2H2) which is used for welding, cutting, and brazing due to its high temperature flame.
- The second image is of Nitrogen (N2) which is used for inerting, blanketing, and purging, as well as in various laboratory and industrial processes.
- The third image is of Propane (C3H8) which is used for heating, cooking, and as a fuel in engines and vehicles.
Keep in mind that if gas cylinders are damaged they can produce great force and spin out of control increasing the potential for injury and damage. Therefore, make sure you understand the ins and outs of compressed gas safety.
2. How Can you Handle Compressed Gas Products Safely?
There are many things you can do as a worker, supervisor, or business owner to make sure you and your co-workers handle compressed gas products safely, such as:
A) Training and Education
- One of the most important things you can do is ensure that all personal involved in handling compressed gas products receive proper training in their safe handling and usage.
- Make sure they understand the properties, hazards, and specific precautions associated with each gas.
B) Leak Detection
- Regularly check for gas leaks using appropriate methods, such as soapy water or gas detectors.
- If a leak is detected, evacuate the area immediately, and follow established emergency procedures.
C) Check the Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
- Each hazardous product will contain an SDS and a label explaining all of the hazards and the necessary precautions for the product being used.
- If you have any questions about this, consult with your supervisor and Joint Health and Safety Committee.
- To lean more about what a safety data sheet is and how to read one, click here.

This is an example of a safety data sheet.
D) Cylinder Inspection
- Regularly inspect cylinders for damage, such as dents, corrosion, or leakage. Do not use damaged cylinders.
- Verify that cylinder labels are clear, accurate, and up-to-date, including information on the gas contents, manufacturer, and safety warnings.
E) Storage and Handling
- Store cylinders in a well-ventilated, dry area that is away from direct sunlight, heat sources, and flammable materials.
- Secure cylinders in an upright position using appropriate restraints or brackets to prevent them from falling or tipping.
- Keep cylinders away from electrical equipment and ignition sources.
F) Transportation
- Use dedicated cylinder carts, dollies, or forklifts to transport cylinders safely. Do not roll or drag them.
- Secure cylinders during transport to prevent movement or falling.
- Ensure cylinders are properly labeled during transportation.

You must be very careful when transporting cylinders containing compressed gas.
G) Valve Operation
- If you need to open cylinder valves do so slowly and fully, do not force them.
- Prior to removing a valve, such as on a propane tank, ensure the tank is completely empty.
- Do not use lubricants or tools on cylinder valves unless recommended by the manufacturer.
- Close cylinder valves tightly when not in use.
H) Ventilation
- Maintain adequate ventilation in areas where compressed gases are used to prevent the accumulation of hazardous gas concentrations.
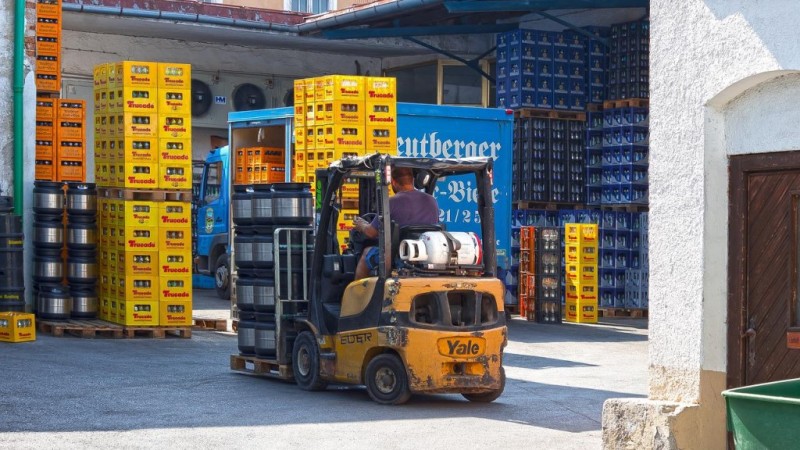
I) Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Provide and ensure the use of appropriate PPE, such as safety glasses, face shields, gloves, or respiratory protection, based on the hazards associated with the gas being handled.
- For refrigerated liquefied gases, wear cold insulated gloves and a face shield or safety glasses. Never wear jewelry as they can freeze to exposed skin.

Wearing the proper PPE will promote compressed gas safety.
J) Regulations and Compliance
- Comply with all relevant local, national, and international regulations and standards governing the handling and transportation of compressed gases.
Handling compressed gas products safely is essential to prevent accidents, protect personnel and property, and ensure the responsible use of these potentially hazardous materials. A strong safety culture and rigorous adherence to safety practices are key to preventing incidents and maintaining a safe working environment.
If you have concerns about your workplaces compressed gas safety, speak with your supervisor or Joint Health and Safety Committee and express your concerns! It is their job to listen and promote safety.
3. What to Do in an Emergency Situation
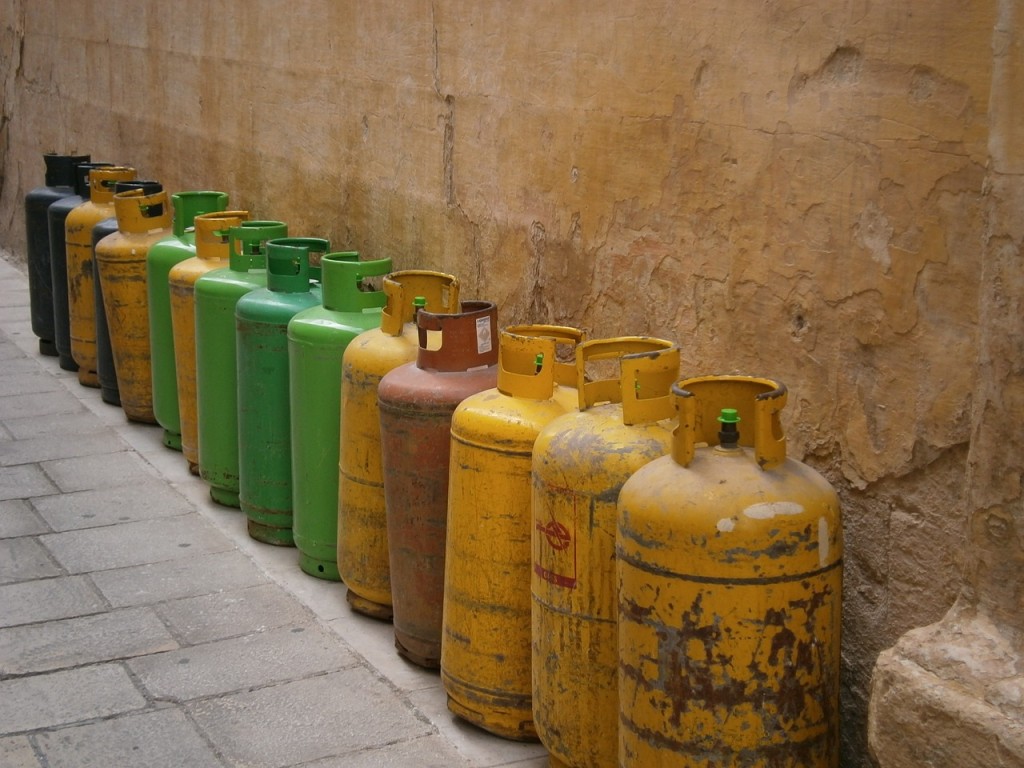

Continue reading to learn what to do in an emergency situation containing compresses gas.
The reason we place so much emphasis on receiving proper compressed gas safety training is because you need to do in an emergency situation and how to prevent them from happening in the first place.
There are several things you should do during an emergency situation, such as:
- Ensure you have fire extinguishers readily available.
- In the event of a fire, have at least two different exit paths.
- Ensure that an emergency shower and eyewash are readily available (test these devices regularly).
- Report leaks to those in charge, warn those around you, and move to a location that is safe.
- Understand the appropriate first aid-measures.
- the CCOHS for instance, recommends that if you come into contact with refrigerated liquefied gases, you should thaw frosted parts with warm water and receive immediate medical attention. They also state that you should not rub the affected area! This may make matters worse.
- When emergency responders arrive, provide them with essential information, including the type of gas involved, the number of cylinders affected, and any relevant safety data sheets (SDS) you have.
- If the situation involves an evacuation take the time to ensure that all personnel have been accounted for and are safe. This can be completed via a simple head count.
It’s crucial to emphasize that safety should always come first, and individuals without the appropriate training and equipment should not attempt to handle gas leaks or fires involving compressed gas cylinders themselves. Follow established emergency response procedures and rely on trained personnel and emergency services to address the situation safely and effectively.
Trust ACUTE Environmental For Safety Training

ACUTE can provide you with compressed gas safety training.
If you are in charge of supervising health and safety in the workplace and are looking for high-quality safety training, book a course with ACUTE. And of course, if you have any questions regarding compressed gas safety, contact us.
Here are some of the benefits of working with ACUTE:
- Open Door Instructor-Student Partnership – ACUTE’s training services emphasize client participation, staff foster relationships with clients and serve as a touchstone for advice anytime moving forward.
- Serving Your Team and Industry – With a vast array of clients in manufacturing, construction, health, academic, and government sectors, ACUTE brings the best safety practices from across the spectrum to your workplace.
- 100 Years Combined Experience – ACUTE provides comprehensive health and safety training, on-site safety services, and consulting services. With over 100 years of combined experience, our company staff offers more than theoretical or abstract ideas. ACUTE offers solutions!
- Track Record of Success – ACUTE is rated 4.9/5 stars on Google reviews, demonstrating our commitment to our clients, our quality, and our passion for training.
What Our Customers Are Saying…
We were referred to ACUTE on behalf of our employer for an n95 mask fitting – the staff here are professional, personable, and informative.
I’d come back here for any safety-related training in a heartbeat.
Acute has been a staple in supporting my companies over the years and have always delivered quality and dependable service. Training programs are top shelf and a great facility for practical application. couldn’t recommend them more. keep up the great work folks.
Outstanding service provided by Acute, right from the customer support end, right through to the delivery of the session. Always professional, quick to respond, and always delivering services that exceed my expectations. Acute has an amazing team that is always helping us achieve better health and safety performance. So are grateful to have such a tremendous resource in Acute!
Hours of Operation and Contact Information:
Monday-Friday: 8:00 AM – 5:00 PM
Saturday-Sunday: Closed
Phone: (519) 747-5075
Fax: (519) 747-4608
Email: info@acuteservices.com

